Product Description
High Power 25HP Electric AC Induction Motor
1. Output power:0.18~200KW
2. Main Materials
Motor shell main materials is ADC Aluminum, cold-rolled sheet, F class high-temperature enameled wire, high strength screw plating color, 40 Gr chrome steel rotor spindle, appearance surface powder coating process, wear-resistant, high temperature resistant, not ordinary paint.
3. Applications
Using voltage range width is suitable for many countries demands, no need extra customized
1)220/380/400/415V–50HZ
2)440V/460V/–60HZ
Achieve national energy saving level 3 energy efficiency.
Motor technical indications meet Europe Efficient Motor Standard.
Rotor shaft head blackening processing and anti-rust performance more powerful, fashion, crust and durable.
Comply with technical indications of CE and China CCC.
4. Products characteristics
Motor appearance: unique appearance design, activities foot, flexible assembly, various installation type.
Mounting type:
B3–horizontal
B5–big flange vertical
B14–small flange vertical
B35–horizontal/vertical mounted
B34–foot small flange mounting
Special appearance is helpful for heat dissipation cooling, modular design is more convenient to use and maintenance.
5. Dimensions
Customization according to the application.
6. Motor main technical indications:
Motor adopts to full closed structure, protection grade can up to IP55
F-class insulation class
The maximum temperature up to 150ºC
B-Level temperature assessment
Low vibration and low noise
7. Perform Standard
All universal motor implementation of uniform production standards:
–Motor power class and dimensions: GB4826-84,GB4772.2-84,IEC72
–Motor criterion: GB755-87,IEC34-1
–Structure and mount type: GB997-81,IEC34-7
–Shell protection level: GB4942.1-85,IEC34-5
–Cooling methods: GB/T1993-93,IEC34-6
8.Product pictures:
9.Technical Data
| Output Power |
0.06~7.5KW |
| Poles |
2poles, 4poles, 6poles, 8poles |
| Frequency |
50HZ or 60HZ, 50HZ & 60HZ |
| Shell Protection Class |
IP54 or IP55 |
| Insulation Classes |
F |
| Installation Form | Foot or Flange can be changed freely |
| Bearing |
C&U, NSK, SKF |
| Color | RAL 5571 blue or silvery white or customized |
10.Our company :
11.Customer visiting:
12.FAQ:
1.Q:What kinds of gearbox can you produce for us?
A:Main products of our company: UDL series speed variator,RV series worm gear reducer, ATA series shaft mounted gearbox, X,B series gear reducer,
P series planetary gearbox and R, S, K, and F series helical-tooth reducer, more
than 1 hundred models and thousands of specifications
2.Q:Can you make as per custom drawing?
A: Yes, we offer customized service for customers.
3.Q:What is your terms of payment ?
A: 30% Advance payment by T/T after signing the contract.70% before delivery
4.Q:What is your MOQ?
A: 1 Set
Welcome to contact us for more detail information and inquiry.
If you have specific parameters and requirement for our gearbox, customization is available. /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Industrial |
|---|---|
| Speed: | Low Speed |
| Number of Stator: | Three-Phase |
| Function: | Driving |
| Casing Protection: | Protection Type |
| Number of Poles: | 2poles, 4poles, 6poles, 8poles |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
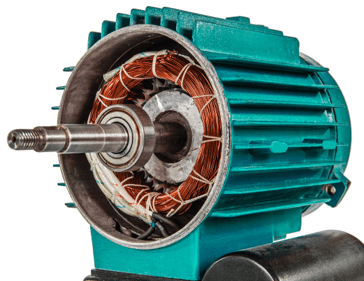
What maintenance practices are essential for prolonging the lifespan of an induction motor?
Maintaining induction motors is crucial for ensuring their longevity and optimal performance. Here are some essential maintenance practices that can help prolong the lifespan of an induction motor:
- Regular Inspections:
- Perform routine visual inspections of the motor to check for any signs of wear, damage, or loose connections.
- Inspect the motor’s ventilation system, cooling fans, and air filters to ensure proper airflow for cooling.
- Look for any abnormal vibrations, unusual noises, or overheating during operation.
- Cleaning and Lubrication:
- Keep the motor clean by removing dust, dirt, and debris that may accumulate on the motor’s surfaces and cooling fins.
- Regularly lubricate the motor’s bearings as per the manufacturer’s recommendations to reduce friction and wear.
- Ensure that the lubrication used is compatible with the motor’s bearing type and operating conditions.
- Monitoring and Testing:
- Monitor the motor’s operating parameters such as voltage, current, power factor, and temperature using appropriate instrumentation.
- Conduct periodic electrical tests, such as insulation resistance tests and winding resistance measurements, to detect any insulation deterioration or anomalies in the motor’s electrical circuit.
- Perform vibration analysis and motor signature analysis to identify potential mechanical issues or faults in the motor’s components.
- Belt and Coupling Maintenance:
- If the motor is coupled to driven equipment using belts or couplings, regularly inspect and adjust the tension of the belts or couplings to ensure proper power transmission.
- Replace worn-out or damaged belts and couplings promptly to prevent excessive vibrations or misalignments that can affect the motor’s performance.
- Protection and Enclosure:
- Ensure that the motor is adequately protected from environmental factors such as dust, moisture, and corrosive substances.
- Verify that the motor’s enclosure or housing is intact and provides sufficient protection against ingress of foreign materials.
- Consider installing additional protective measures, such as motor covers or guards, if the motor operates in harsh or hazardous environments.
- Corrective Maintenance:
- Promptly address any identified issues or abnormalities in the motor’s performance through corrective maintenance.
- Repair or replace faulty components, such as bearings, windings, or capacitors, using genuine replacement parts recommended by the motor manufacturer.
- Engage qualified technicians or electricians for complex repairs or rewinding tasks to ensure proper handling of the motor.
- Documentation and Record-Keeping:
- Maintain comprehensive records of the motor’s maintenance activities, including inspection reports, test results, repairs, and replacements.
- Track the motor’s history and performance trends to identify any recurring issues or patterns that may require special attention.
- Use the documentation and records as a reference for future maintenance and as a resource for troubleshooting or warranty claims.
Adhering to these maintenance practices can significantly extend the lifespan of an induction motor and ensure its reliable operation over time. Regular inspections, cleaning, monitoring, and timely corrective actions are key to preventing major failures and optimizing the motor’s performance.

What safety precautions should be followed when working with induction motors?
Working with induction motors requires adherence to proper safety precautions to minimize the risk of accidents, injuries, or equipment damage. Here are some important safety precautions to follow:
- Electrical Safety:
- Always de-energize the motor and ensure the power source is disconnected before working on or near the motor.
- Use lockout/tagout procedures to secure the power source and prevent accidental energization during maintenance or repair work.
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as insulated gloves, safety glasses, and electrical-rated footwear when working with live electrical components.
- Follow electrical safety guidelines and local regulations when installing, wiring, or troubleshooting induction motors.
- Ensure that the motor’s electrical connections are properly insulated and protected against accidental contact or short circuits.
- Mechanical Safety:
- Avoid wearing loose clothing, jewelry, or anything that can get entangled in moving parts of the motor.
- Use machine guards, safety shields, or barriers to prevent accidental contact with rotating shafts, belts, or other hazardous motor components.
- Ensure that the motor is securely mounted or fastened to prevent it from shifting or falling during operation.
- Never reach into a running motor or attempt to make adjustments while the motor is in operation.
- Allow the motor to come to a complete stop and wait for any residual motion to cease before performing maintenance tasks.
- Heat and Ventilation:
- Induction motors can generate heat during operation.
- Avoid touching hot motor surfaces and allow sufficient cooling time before carrying out maintenance or inspection tasks.
- Ensure that the motor’s ventilation system, including fans and cooling fins, is clean and unobstructed to prevent overheating.
- Follow manufacturer guidelines for proper motor ventilation and cooling requirements.
- Safe Lifting and Handling:
- Induction motors can be heavy and require proper lifting and handling techniques.
- Use appropriate lifting equipment and techniques to prevent strains or injuries when moving or installing motors.
- Follow safe lifting practices and weight limits specified by the motor manufacturer.
- Engage additional personnel or equipment if necessary to safely handle large or bulky motors.
- Qualified Personnel:
- Ensure that only qualified personnel with proper training and knowledge of induction motors are involved in installation, maintenance, or repair tasks.
- Engage licensed electricians or technicians familiar with electrical safety procedures and motor handling practices.
- Refer to motor-specific documentation, manuals, and guidelines provided by the manufacturer for proper handling, maintenance, and safety recommendations.
- Documentation and Safety Guidelines:
- Maintain records of motor-related safety procedures, maintenance activities, and incidents for future reference and continuous improvement.
- Follow safety guidelines established by regulatory authorities, industry standards, and the organization’s safety policies.
- Regularly review and update safety procedures and provide training to personnel to ensure awareness of safe practices when working with induction motors.
These safety precautions are essential for protecting personnel, preventing accidents, and maintaining a safe working environment when working with induction motors. It is crucial to prioritize safety at all times and comply with applicable safety regulations to mitigate risks associated with motor operation and maintenance.
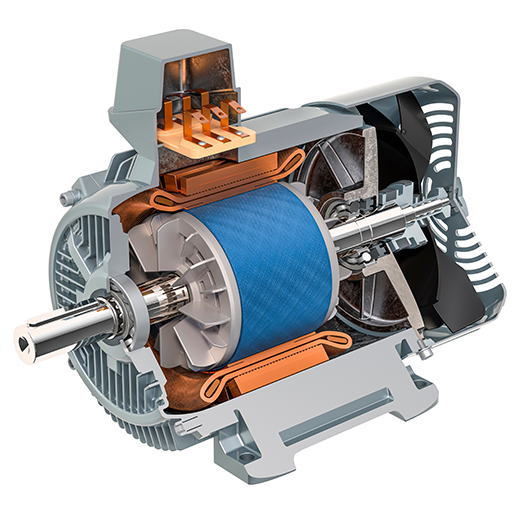
How do induction motors differ from other types of electric motors?
Induction motors differ from other types of electric motors in several ways. Here’s a detailed explanation of the key differences:
- Operating Principle:
- Induction motors operate based on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where a rotating magnetic field induced by the stator windings interacts with the rotor conductors to produce torque.
- In contrast, other types of electric motors, such as DC motors, synchronous motors, and stepper motors, operate on different principles and have distinct mechanisms for generating motion.
- Power Supply:
- Induction motors typically operate on AC (alternating current) power supply. The stator windings are connected to an AC power source, which produces a rotating magnetic field.
- On the other hand, DC motors require a DC power supply, and synchronous motors may operate on either AC or DC power supply, depending on their design.
- Speed Control:
- Induction motors have a fixed speed determined by the frequency of the AC power supply and the number of poles in the motor. The speed can be adjusted to some extent by changing the supply frequency or using variable frequency drives (VFDs).
- DC motors, on the other hand, offer precise speed control by adjusting the voltage applied to the motor armature.
- Synchronous motors can operate at a fixed speed determined by the frequency of the AC power supply, but they can also be controlled using specialized techniques such as field weakening or using electronic drives.
- Stepper motors operate in discrete steps, allowing precise control of position and speed.
- Construction:
- Induction motors are typically constructed with a squirrel cage rotor, which consists of short-circuited conductive bars or loops. The rotor construction makes them simple, robust, and suitable for high-speed applications.
- Other types of motors may have different rotor constructions, such as wound rotors in some AC motors or permanent magnets in brushless DC motors.
- Starting Mechanism:
- Induction motors are self-starting, meaning they can start without the need for additional starting mechanisms. The rotating magnetic field generated by the stator windings induces voltage and current in the rotor, enabling the motor to start rotating.
- Some other types of motors, such as DC motors, require external starting mechanisms like starting resistors or electronic controls to initiate rotation.
- Efficiency and Maintenance:
- Induction motors are known for their high efficiency and low maintenance requirements. They have a simple construction with no brushes or commutators, which reduces wear and eliminates the need for regular maintenance.
- Other types of motors, such as brushed DC motors, may require brush replacement and periodic maintenance.
These are some of the main differences between induction motors and other types of electric motors. Each type of motor has its advantages, disadvantages, and specific applications, depending on the requirements of the system or industry where they are used.


editor by CX 2024-04-17